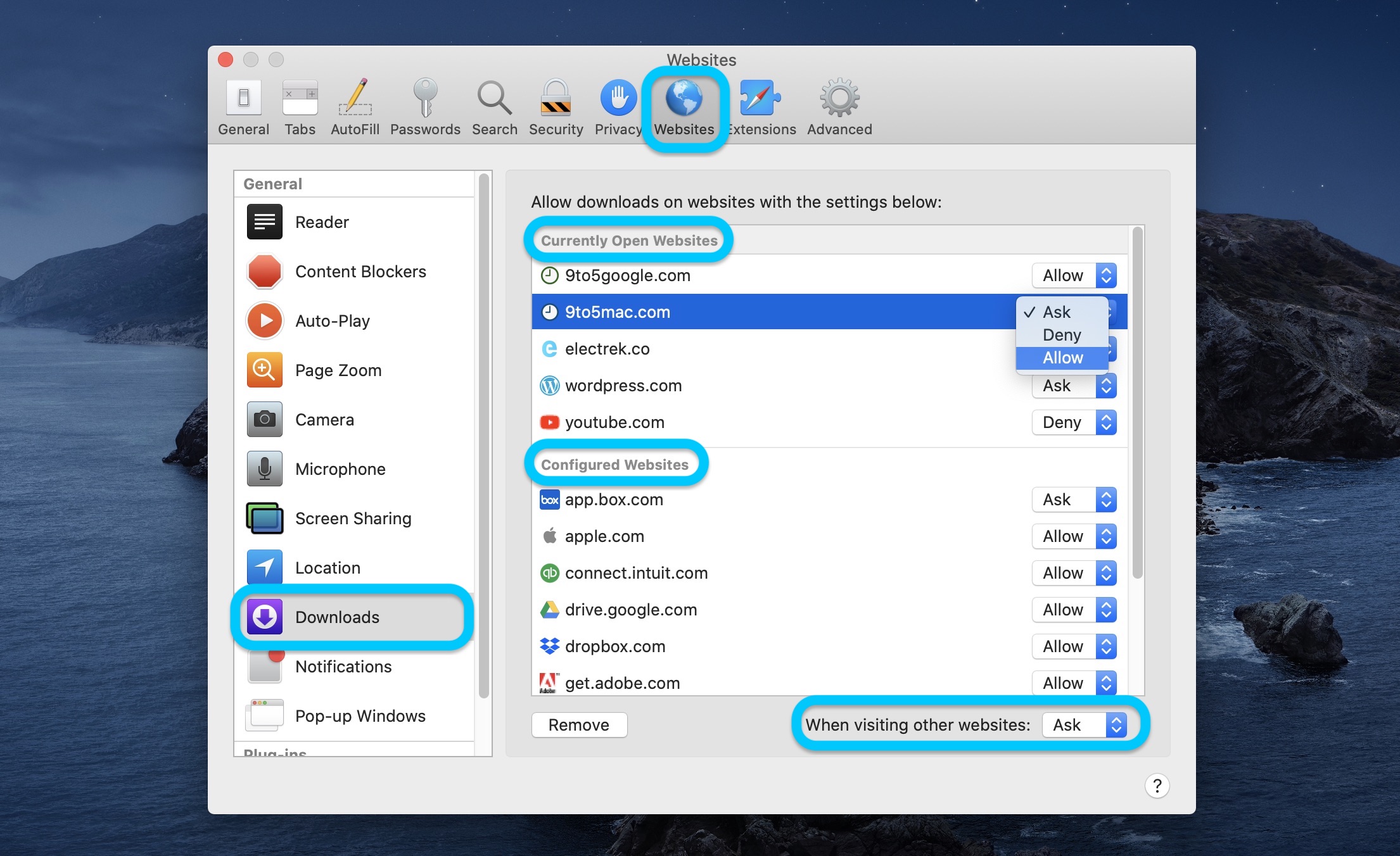
Mac: How to always allow downloads in Safari. Open Safari on your Mac. Click Safari in the menu bar (top left corner) then choose Preferences. At the top of the window, click Websites. Aug 05, 2012 The safest approach is to look for a later version of the app from the Mac App Store or look for an alternative app. To override your security settings and open the app anyway: In the Finder, locate the app you want to open. Don’t use Launchpad to do this. Launchpad doesn’t allow you to access the shortcut menu.
- Allow Downloads On Microsoft Edge
- How To Allow Downloads On Macbook
- Allow Download Ie
- How To Allow Downloads On Mac
- How To Allow Safari Downloads On Mac
At the bottom of the window, you’ll see multiple options under Allow apps to be downloaded from. Select Anywhere to allow your Mac to download any and all apps. If you later decide that you’d like to return to your Mac’s default settings and no longer allow apps to be downloaded from anywhere, just follow these steps: Launch Terminal. To enable your app to connect to a server process running on another machine (or on the same machine), enable outgoing network connections. To enable opening a network listening socket so that other computers can connect to your app, allow incoming network connections. Why the Allow Button is not Working when App is Blocked from Loading on Your Mac The secret is in any other user accounts that you have on your Mac. Even if you have not created any account for any other user, you at minimum may well have a ‘Guest’ account, even if you did not set one up ( read here to read more about that guest account. Select the 'General' tab, and select the lock in the lower left corner to allow changes. Enter your computer username and password, then select 'Unlock.' In the 'Allow apps downloaded from:' section, select the radio button to the left of 'Anywhere.' Close the window. You can now install unsigned applications that you trust. Neither is the app I need to allow acces. Where did the apps go and how can I fix this? Thanks a bunch for any assistance!! Not all apps can/allow you to post to said app directly from the camera roll like facebook. Otherwise you would need to go to said app - and then choose your pics from your camera roll like instagram.
Note: This chapter describes property list keys specific to the macOS implementation of App Sandbox. They are not available in iOS.
In your macOS Xcode project, configure fine-grained security permissions by enabling settings in the Summary tab of the target editor. These settings, in turn, add Boolean values to entitlement keys in the target’s .entitlementsproperty list file. The values are then incorporated into the target’s code signature when you build the project.
You can think of using App Sandbox entitlements as a two-step process:
Sandbox a target, which removes most capabilities for interacting with the system
Restore capabilities to the sandboxed target, as needed, by configuring App Sandbox entitlements
At runtime, if a target requires a capability or a system resource for which the target isn’t entitled, the sandbox daemon (sandboxd) logs a violation message to the console.
For more information about App Sandbox, read App Sandbox Design Guide.
App Sandbox Entitlement Keys
This section describes the keys you can use to confer capabilities to a sandboxed app in macOS. The first key enables App Sandbox; the others configure the sandbox. If App Sandbox is not enabled, the other keys in this section are meaningless.
The value to use for any of these keys is a Boolean YES or NO, with the default value in each case being NO. If you are editing the .entitlements file directly in a text editor, the corresponding Boolean values to use are <true/> and <false/>. The default value for each key is false, so you can (and generally should) leave out the entitlement entirely rather than specifying a false value.
In cases where there are read-only and read/write entitlement key pairs, use of either key in the pair is mutually exclusive with the other.
Add these keys by using the Summary tab of the Xcode target editor. You can also add them directly to a target’s .entitlements file with the Xcode property list editor.
For information on additional entitlements for handling special circumstances, see App Sandbox Temporary Exception Entitlements.
For each key in this table, providing a Boolean value of YES enables the corresponding capability (unless otherwise noted).
Enables App Sandbox for a target in an Xcode project
Allows access to group containers that are shared among multiple apps produced by a single development team, and allows certain additional interprocess communication between the apps
Supported in macOS v10.7.5 and in v10.8.3 and later. The format for this attribute is described in Adding an App to an App Group.
Read-only access to the user’s Movies folder and iTunes movies
For details, see Enabling Access to Files in Standard Locations.
Read/write access to the user’s Movies folder and iTunes movies
For details, see Enabling Access to Files in Standard Locations.
Read-only access to the user’s Music folder
For details, see Enabling Access to Files in Standard Locations.
Read/write access to the user’s Music folder
For details, see Enabling Access to Files in Standard Locations.
Read-only access to the user’s Pictures folder
For details, see Enabling Access to Files in Standard Locations.
Allow Downloads On Microsoft Edge
Read/write access to the user’s Pictures folder
For details, see Enabling Access to Files in Standard Locations.
Communication with AVB devices
For details, see Enabling Hardware Access.
Interaction with Bluetooth devices
For details, see Enabling Hardware Access.
Capture of movies and still images using the built-in camera, if available
For details, see Enabling Hardware Access.
Interaction with FireWire devices (currently, does not support interaction with audio/video devices such as DV cameras)
For details, see Enabling Hardware Access.
Recording of audio using the built-in microphone, if available, along with access to audio input using any Core Audio API that supports audio input
For details, see Enabling Hardware Access.
Interaction with serial devices
Allow App Anywhere Mac
For details, see Enabling Hardware Access.
Interaction with USB devices, including HID devices such as joysticks
For details, see Enabling Hardware Access.
Read/write access to the user’s Downloads folder
For details, see Enabling Access to Files in Standard Locations.
Use of app-scoped bookmarks and URLs
For details, see Enabling Security-Scoped Bookmark and URL Access.
Use of document-scoped bookmarks and URLs
For details, see Enabling Security-Scoped Bookmark and URL Access.
Read-only access to files the user has selected using an Open or Save dialog
How To Allow Downloads On Macbook
For details, see Enabling User-Selected File Access.
Read/write access to files the user has selected using an Open or Save dialog
For details, see Enabling User-Selected File Access.
Allows apps to write executable files.
For details, see Enabling User-Selected File Access.
Child process inheritance of the parent’s sandbox
Allow Download Ie
For details, see Enabling App Sandbox Inheritance.
Network socket for connecting to other machines
How To Allow Downloads On Mac
For details, see Enabling Network Access.
Network socket for listening for incoming connections initiated by other machines
For details, see Enabling Network Access.
com.apple.security.personal-information.addressbook
Read/write access to contacts in the user’s address book; allows apps to infer the default address book if more than one is present on a system
For details, see Enabling Personal Information Access.
Read/write access to the user’s calendars
For details, see Enabling Personal Information Access.
Use of the Core Location framework for determining the computer’s geographical location
For details, see Enabling Personal Information Access.
Printing
For details, see Enabling Hardware Access.
Ability to use specific AppleScript scripting access groups within a specific scriptable app
For details, see Enabling Scripting of Other Apps.
Enabling App Sandbox
You enable App Sandbox individually for each target in an macOS Xcode project. For example, you may design a project as a main app, and some helpers in the form of XPC services. You then enable and configure the sandbox for each target individually.
To learn how to enable App Sandbox for your macOS app, which includes performing code signing, see App Sandbox Quick Start in App Sandbox Design Guide. The essential step is to ensure that the target editor checkbox named in Table 4-1 is selected.
Setting | Entitlement key |
|---|---|
Enable App Sandboxing |
|
Enabling User-Selected File Access
Xcode provides a pop-up menu, in the Summary tab of the target editor, with choices to enable read-only or read/write access to files and folders that the user explicitly selects. When you enable user-selected file access, you gain programmatic access to files and folders that the user opens using an NSOpenPanel object, and files the user saves using an NSSavePanel object.
Certain other user interactions, such as dragging items to your app or choosing items from the Open Recent menu, automatically expand your sandbox to include those items. Similarly, when macOS resumes an app after a reboot, the sandbox is automatically expanded to include any items that are automatically opened.
To enable user-selected file access in your app, use the Xcode target editor setting shown in Table 4-2.
Note: If your app needs to create executable files that are typically executed in some way other than through Launch Services (shell scripts, for example), you should also specify the com.apple.security.files.user-selected.executable entitlement.
By default, when writing executable files in sandboxed apps, the files are quarantined. Gatekeeper prevents quarantined executable files and other similar files (shell scripts, web archives, and so on) from opening or executing unless the user explicitly launches them from Finder.
If those executables are tools that are intended to run from the command line, such as shell scripts, this presents a problem. With this flag, the file quarantine system allows the app to write non-quarantined executables so that Gatekeeper does not prevent them from executing.
This entitlement does not have an Xcode checkbox, and thus must be added to your app’s entitlement property list manually. For details, see App Sandbox Entitlement Keys.
Setting | Entitlement keys |
|---|---|
User Selected File |
|
Enabling Access to Files in Standard Locations
In addition to granting user-selected file access, you can employ entitlements to grant programmatic file access to the following user folders:
Downloads
Music
Movies
Pictures
The Xcode control for enabling Downloads folder access is a checkbox; the controls for enabling access to these other folders are pop-up menus.
When you enable programmatic access to the user’s Movies folder, you also gain access to their iTunes movies.
Reopening of files by macOS using Resume does not require the presence of any entitlement key.
To enable programmatic access to specific folders, use the Xcode target editor settings shown in Table 4-3.
Setting | Entitlement keys |
|---|---|
Downloads Folder |
|
Music Folder |
|
Movies Folder |
|
Pictures Folder |
|
Enabling Security-Scoped Bookmark and URL Access
If you want to provide your sandboxed app with persistent access to file system resources, you must enable security-scoped bookmark and URL access. Security-scoped bookmarks are available starting in macOS v10.7.3.
How To Allow Safari Downloads On Mac
To add the bookmarks.app-scope or bookmarks.document-scope entitlement, edit the target’s.entitlementsproperty list file using the Xcode property list editor. Use the entitlement keys shown in Table 4-4, depending on which type of access you want. Use a value of <true/> for each entitlement you want to enable. You can enable either or both entitlements.
For more information on security-scoped bookmarks, read Security-Scoped Bookmarks and Persistent Resource Access in App Sandbox Design Guide.
Entitlement key | Description |
|---|---|
| Enables use of app-scoped bookmarks and URLs |
| Enables use of document-scoped bookmarks and URLs. Version note: in macOS v10.7.3, this entitlement key was named |
Enabling Network Access
Xcode’s Network checkboxes in the Summary tab of the target editor let you enable network access for your app.
To enable your app to connect to a server process running on another machine (or on the same machine), enable outgoing network connections.
To enable opening a network listening socket so that other computers can connect to your app, allow incoming network connections.
Note: Both outgoing and incoming connections can send and receive data. The sole difference is in whether your app is initiating the connection or is receiving connections initiated by other apps or other hosts.
To enable network access, use the Xcode target editor settings shown in Table 4-5.
Setting | Entitlement key |
|---|---|
Allow Incoming Connections |
|
Allow Outgoing Connections |
|
Enabling Hardware Access
To allow a sandboxed target to access hardware services on a system—USB, printing, or the built-in camera and microphone—enable the corresponding setting in the Summary tab of the Xcode target editor.
Camera access enables access to video and still image capture using the built-in camera, if available.
Microphone access enables access to audio recording using the built-in microphone, if available.
USB access enables the ability to interact with USB devices using USB device access APIs. On violation,
sandboxdnames the I/O Kit class your code tried to access.Printing access is required if you want to provide a target with the ability to print.
To enable access to hardware, use the Xcode target editor settings shown in Table 4-6.
Setting | Entitlement key |
|---|---|
Allow Camera Access |
|
Allow Microphone Access |
|
Allow USB Access |
|
Allow Printing |
|
To allow access to hardware devices for which no checkbox exists in Xcode’s user interface, you must manually add the appropriate entitlement to your app’s entitlements property list. These additional entitlements are listed in Table 4-7. All of these keys take a Boolean value.
Entitlement key | Description |
|---|---|
| Interaction with AVB devices by using the Audio Video Bridging framework |
| Interaction with Bluetooth devices |
| Interaction with FireWire devices (currently, does not support interaction with audio/video devices such as DV cameras) |
| Interaction with serial devices |
Enabling Personal Information Access
A user’s personal information is inaccessible to your sandboxed app unless you grant access using the appropriate settings.
Address Book access enables read/write access to contacts in the user’s address book.
Location Services access enables use of the Core Location framework to determine the computer’s geographic position.
Calendar access enables read/write access to the user’s calendars.
To enable access to personal information, use the Xcode target editor settings shown in Table 4-8.
Setting | Entitlement key |
|---|---|
Allow Address Book Data Access |
|
Allow Location Services Access |
|
Allow Calendar Data Access |
|
Adding an App to an App Group
The com.apple.security.application-groups (available in macOS v10.7.5 and v10.8.3 and later) allows multiple apps produced by a single development team to share access to a special group container. This container is intended for content that is not user-facing, such as shared caches or databases.
In addition, this attribute allows the apps within the group to share Mach and POSIX semaphores and to use certain other IPC mechanisms among the group’s members. For additional details and naming conventions, read “Mach IPC and POSIX Semaphores and Shared Memory” in App Sandbox Design Guide.
The value for this key must be of type array, and must contain one or more string values, each of which must consist of your development team ID, followed by a period, followed by an arbitrary name chosen by your development team. For example:
The group containers are automatically created or added into each app’s sandbox container as determined by the existence of these keys. The group containers are stored in ~/Library/Group Containers/<application-group-id>, where <application-group-id> is one of the strings from the array. Your app can obtain the path to the group containers by calling the containerURLForSecurityApplicationGroupIdentifier: method of NSFileManager.
Enabling App Sandbox Inheritance
If your app employs a child process created with either the posix_spawn function or the NSTask class, you can configure the child process to inherit the sandbox of its parent. However, using a child process does not provide the security afforded by using an XPC service.
Important: XPC (as described in External Tools, XPC Services, and Privilege Separation) complements App Sandbox and is the preferred technology for implementing privilege separation in an macOS app. Before using a child process, consider using an XPC service instead.
To enable sandbox inheritance, a child target must use exactly two App Sandbox entitlement keys: com.apple.security.app-sandbox and com.apple.security.inherit. If you specify any other App Sandbox entitlement, the system aborts the child process. You can, however, confer other capabilities to a child process by way of iCloud and notification entitlements.
The main app in an Xcode project must never have a YES value for the inherit entitlement.
To add the inherit entitlement, edit the target’s .entitlementsproperty list file using the Xcode property list editor. Use the entitlement key shown in Table 4-9 with a value of <true/>.
Note: This property causes the child process to inherit only the static rights defined in the main app’s entitlements file, not any rights added to your sandbox after launch (such as PowerBox access to files).
If you need to provide access to files opened after launch, you must either pass the data to the helper or pass a bookmark to the child process. The bookmark need not be a security-scoped bookmark, but it can be, if desired.
If you are using other APIs to create child processes (such as NSWorkspace) and wish to have a shared container directory, you must use an app group.
Entitlement key | Description |
|---|---|
| Enables App Sandbox inheritance |
Enabling Scripting of Other Apps
If your app needs to control another scriptable app, your app can use the scripting targets entitlement to request access to one or more of the scriptable app’s scripting access groups.
Note: Before you can use this entitlement, the scriptable app must provide scripting access groups. If it does not, you can still control the app, but you use a temporary exception entitlement instead. In some cases, you may use both scripting-targets entitlement and a temporary entitlement together, to provide support across different versions of the OS. For more information, see Apple Event Temporary Exception.
Entitlement key | Description |
|---|---|
| Ability to use specific AppleScript scripting access groups within a specific scriptable app |
The scripting target entitlement contains a dictionary where each entry has the target app’s code signing identifier as the key, and an array of scripting access groups as the value. Scripting access groups are identified by strings and are specific to an app. For example, the following entry would grant access to composing mail messages with Apple’s Mail app:
For more information about how to add scripting access groups to an app, watch WWDC 2012: Secure Automation Techniques in OS X and read the manual page for sdef.
Copyright © 2017 Apple Inc. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use Privacy Policy Updated: 2017-03-27
Apple is obsessed with privacy and security which is a good thing for us, the end-users. By default, macOS allows you to only run apps and software that are downloaded from the Mac App Store or identified developers. But if you want to open an app from an unidentified developer in macOS, then here are two ways to do so.
However, before we begin, a word of caution! It is a common and prevalent practice to insert harmful code and malware into apps and distribute/redistribute them. So, it is quite possible that a shady app that you torrented or got from an unverified developer might be infected and dangerous. If you understand the consequences and still want to proceed, here is how to override your security settings and open an app anyway from the unidentified developer in macOS.
How to Allow and Open App from Unidentified Developer in macOS
Step #1. Launch Finder on your Mac and locate the app you want to open. You are most likely to find this app in Downloads, Desktop or Applications folder.
Note: Do not use Launchpad as Launchpad does not allow a shortcut menu on apps.
Step #2.Control-click (hold the Control button and click) on the app icon.
Step #3. Now click on Open from the above list. Confirm if asked again to whether open the app or not.
You will see that the unidentified app has opened. From now onwards, this app is saved as an exception to your security settings. Anytime in the future, you can open it by double-clicking just like you open other known and registered apps. As mentioned in the previous line, this does not change the whole relevant security settings of your Mac but merely creates an exception for this particular app. Everything else is just as secure as it was.
Additional Method: If you don’t follow the above steps and simply double click an unidentified app and it does not open and shows a popup similar to the one below.
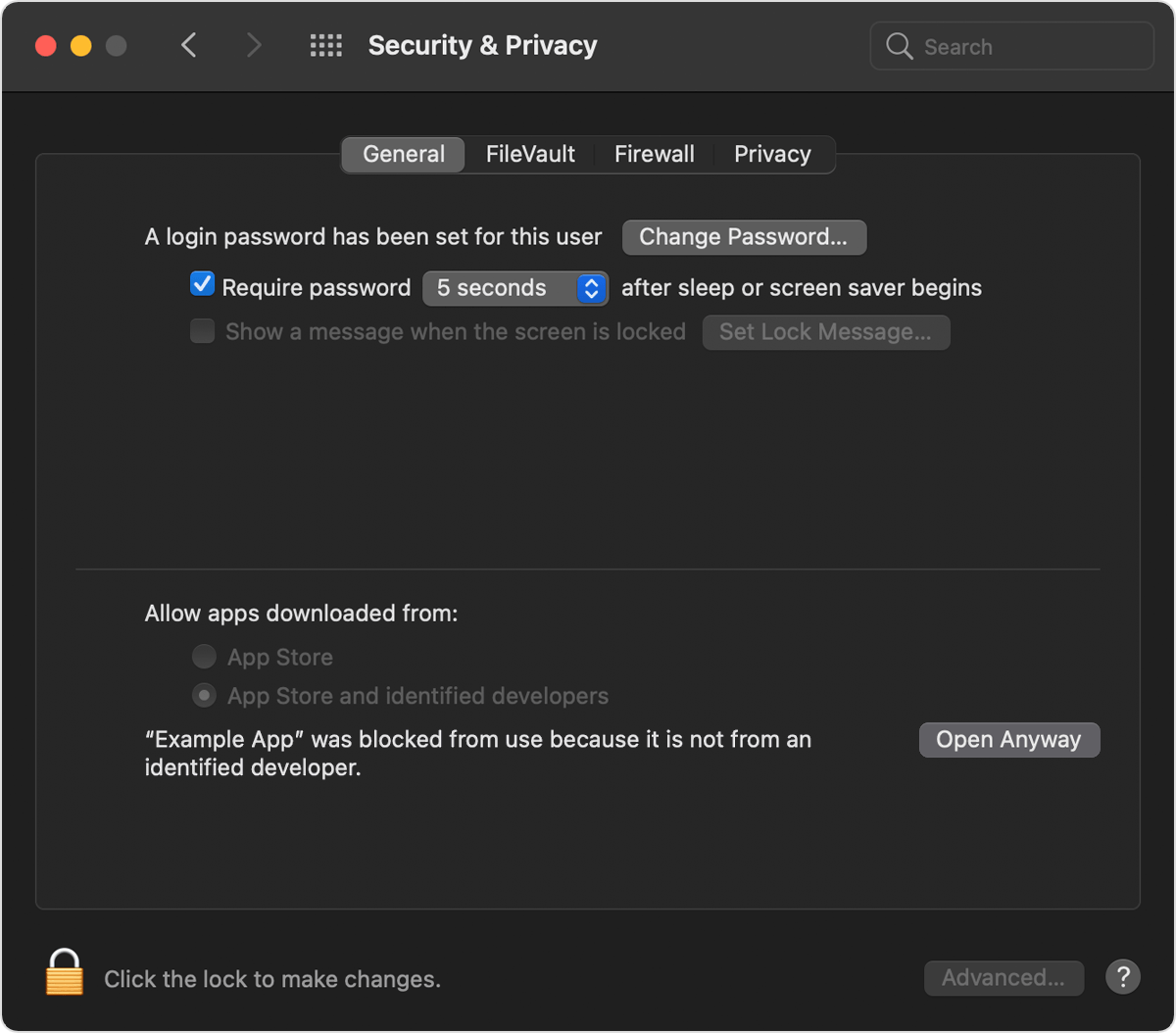
Go to System Preferences – Security and Privacy and click on the Open Anyway option. Enter your Mac’s password if asked.
The above methods were relatively secure, easy, and swift to open an unidentified app. It hardly took a few clicks. However, if you would like to change the security settings of your Mac (as far as app launching is concerned), then you will have to disable Gatekeeper and turn on Allow apps downloaded from to: Anywhere.
How to Allow All Unknown Apps to Open on Mac Running macOS Catalina
Step#1. Open Terminal on your Mac by going into Launchpad – Other. Or you may press together Command(⌘) + Space Bar to open Spotlight Search, type Terminal and hit enter.
Step #2. Make sure System Preferences is not open. If it is, close it. In the Terminal type the following command and hit enter.
sudo spctl ––master-disable
Step #3. Enter your Mac’s password and hit enter. Note that when you type the password it won’t be visible. You may close Terminal now.
Step #4. Launch System Preferences from your Dock or by clicking on Apple Logo – System Preferences. Now click on Security and Privacy.
Step #5. Under the General tab, you might see that under ‘Allow apps downloaded from’, ‘Anywhere’ is chosen. If not, then from the bottom left, click on the closed padlock icon and enter your Mac’s Password.
Step #6. From under Allow apps downloaded from: choose Anywhere. Click on Allow From Anywhere to confirm. Click on the open padlock to prevent further changes as our motive has been achieved.
From now onwards your Mac will open all apps irrespective of whether it is downloaded from App Store, App Store and identified developers or any random developer. Please know that this is dangerous for the security and safety of your Mac and your private data. So only do this if you know what you are into. For most ordinary people, it is advised that you do not go this route. Use the first method instead.
To turn Gatekeeper back on and return everything to the default state:
Open Terminal and type the following command and hit the enter key. Input your Mac’s password to confirm.
sudo spctl –master-enable
Are All Apps from Unidentified Developers Dangerous?
No. This is not necessarily the case. As Apple puts it, there may be some apps that were written before developer ID registration began. As a result, the app may not have been reviewed, and thus macOS can’t check whether the app has been modified or broken since it was released. Similarly, suppose you or your developer friend or someone you have been following for long and trust, build a simple app as a hobby. Is it dangerous? No! It is just not registered with Apple.
The safest approach to install an app from an unidentified developer is by finding a similar alternative app from the Mac App Store or identified developer. Sometimes paying for a similar app may also be a sensible solution than using a free unknown app. But if nothing works for you overriding the security settings and allowing apps from unidentified developers in macOS is a solution. In this sense, macOS is more flexible than iOS.
You may like to read:
The founder of iGeeksBlog, Dhvanesh, is an Apple aficionado, who cannot stand even a slight innuendo about Apple products. He dons the cap of editor-in-chief to make sure that articles match the quality standard before they are published.
- https://www.igeeksblog.com/author/dhvanesh/
- https://www.igeeksblog.com/author/dhvanesh/